Introduction
Explainable AI (XAI) is a framework for designing and developing artificial intelligence (AI) systems that can be understood and interpreted by humans. The goal of XAI is to make AI systems transparent and explainable so that end-users can understand how a decision was made, and experts can identify errors or biases in the system. XAI is becoming increasingly important as AI is used in high-stakes decision-making processes, such as medical diagnosis or financial risk assessment, where the consequences of a wrong decision can be significant.
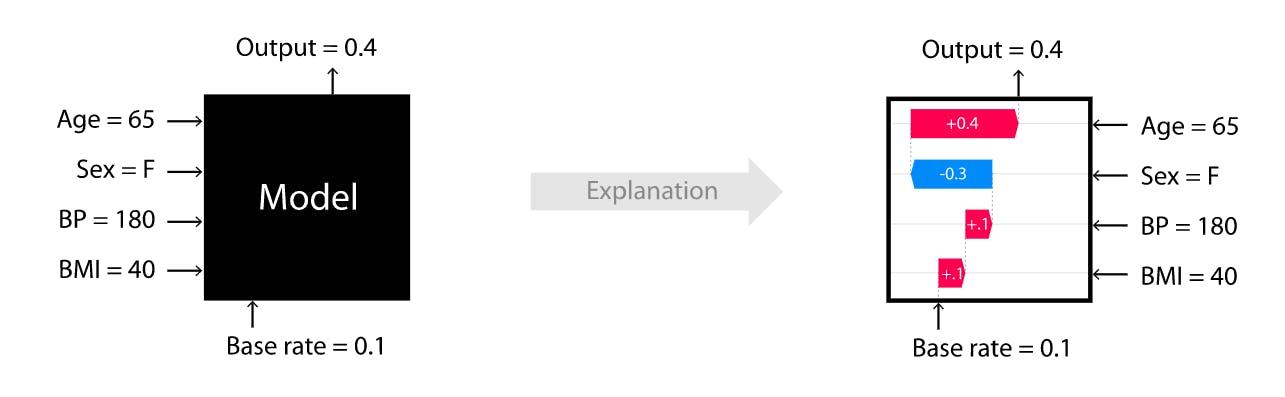
In the context of the Google Cloud Platform (GCP), XAI involves developing models that can provide clear and transparent explanations for their predictions or decisions. GCP provides various tools and services that enable developers to build and deploy explainable AI models, such as the Explainable AI Platform and AutoML Explainable AI. These tools provide features such as model interpretability, feature importance, and explanations for individual predictions.
Importance of XAI
In many real-world applications of AI, it's important to understand how the models are making decisions and to be able to explain those decisions to stakeholders.
In industries like healthcare, finance, and law, for example, it's crucial to be able to justify the decisions made by AI models and to ensure that they're not biased or discriminatory.
Below is an example that tells us the contribution of a pixel (of an image) in a layer, Y-axis is the pixel and X-axis is a measure of contribution.
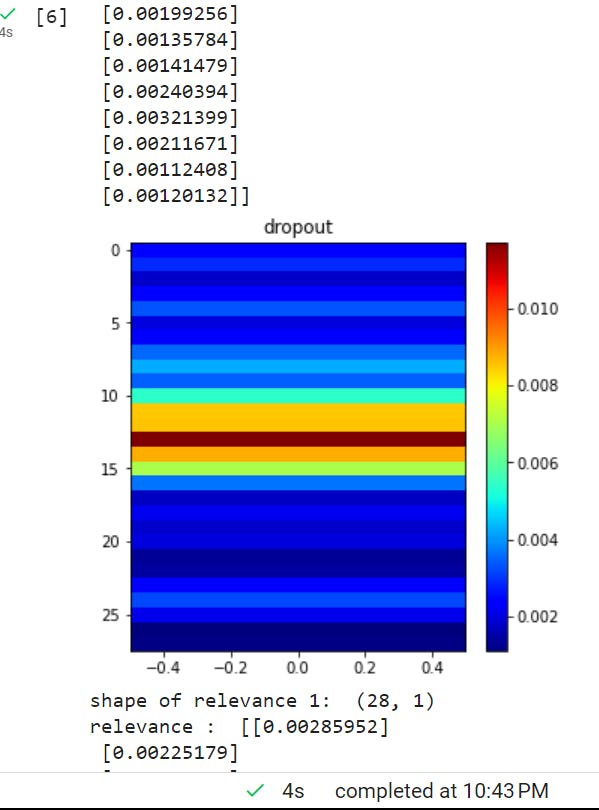
The above is just an example that I have taken from my ongoing project, the key point from here is XAI can tell us each feature contribution in layers/models so that we can improve accuracy.
Sample code
The below code can be seen at https://github.com/slundberg/shap
import transformers
import shap
# load a transformers pipeline model
model = transformers.pipeline('sentiment-analysis', return_all_scores=True)
# explain the model on two sample inputs
explainer = shap.Explainer(model)
shap_values = explainer(["What a great movie! ...if you have no taste."])
# visualize the first prediction's explanation for the POSITIVE output class
shap.plots.text(shap_values[0, :, "POSITIVE"])

Explainable AI tools available in GCP
Below are some of the Explainable AI tools and services available in GCP:
Cloud AutoML: Cloud AutoML is a suite of machine learning tools that allow users to build custom models without needing extensive AI expertise. It includes a range of Explainable AI features, including model interpretation and explanation.
AI Platform: AI Platform is a cloud-based platform for building, testing, and deploying machine learning models. It includes a range of Explainable AI tools and services, such as model explanation, interpretation, and fairness evaluation.
TensorFlow: TensorFlow is an open-source machine learning framework developed by Google. It includes a range of Explainable AI features, including model interpretation and visualization.
Cloud AI Explainability: Cloud AI Explainability is a tool that helps users understand how AI models make decisions. It provides insights into the factors that contribute to model predictions, allowing stakeholders to identify potential biases or errors.
Limitations
As XAI is evolving day by day, its limitations are also reducing gradually but still has the following limitation which needs to be considered: -
Complexity: XAI is limited by the complexity of the underlying machine learning models. As models become more complex, it can be difficult to identify which inputs and decisions led to a particular output, making it challenging to provide a clear explanation.
Trade-Offs: In many cases, XAI requires trade-offs between model performance and explainability. For example, adding interpretability features to a model can often result in a loss of accuracy.
Domain-Specific: Explainable AI methods are often domain-specific, which means that they are designed to provide explanations for a specific type of model or task. This can limit their applicability across different domains.
Limitations of Data: Explainable AI requires access to large amounts of high-quality data to train models, and this can be a limitation in certain domains where data is scarce or sensitive.
Conclusion
In conclusion, as AI continues to evolve, the importance of Explainable AI cannot be overstated. With GCP's robust suite of Explainable AI tools and services, users can ensure that their AI systems are transparent, interpretable, and fair, providing a solid foundation for building trust in AI.

