Table of contents
Introduction
I'm going to tell you how you can see an article's sentiment(rated from -1 to 1). This blog is focusing on fetching the data from a hashnode account, storing it in a BigQuery table and using NLP to measure the sentiment of each article through its title.
Pre-requisites
You should have a GCP account, with a service account(recommended).
Must have a hashnode account through which you can access Personal Access Token.

Procedure and Code
- Import all necessary libraries
>>> import requests
>>> from google.cloud import bigquery
>>> from google.oauth2 import service_account
>>> from textblob import TextBlob
- Use your service account to make a connection with the BigQuery table.
>>> credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file('service_account.json')
>>> client = bigquery.Client(credentials=credentials, project='project-id')
- Define a function to extract articles from hashnode API. Please change the username, and keep the username from which you are going to fetch articles.
>>> def extract_articles():
# Set up Hashnode API endpoint
hashnode_api_endpoint = "https://api.hashnode.com"
# Define Hashnode API query
query = '''
query {
user(username: "rohan-anand") {
publication {
posts {
_id
title
slug
dateAdded
}
}
}
}
'''
# Set up Hashnode API headers
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "personal-access-token"
}
# Send query to Hashnode API
response = requests.post(hashnode_api_endpoint, headers=headers, json={'query': query})
if response.status_code == 200: # 200 tells connection is 'ok'
articles = response.json()['data']['user']['publication']['posts']
return articles
else:
raise ValueError(f"Failed to retrieve articles: {response.content}")
- Make a function to analyze sentiment using NLP, in the below codes return sentiment on a scale of -1 to 1 means -1=very negative, 0=neutral, and 1=very positive.
>>> def analyze_articles(articles):
analyzed_articles = []
for article in articles:
# TextBlob is used for extracting keywords from article content
blob = TextBlob(article['title'])
keywords = blob.noun_phrases
# Extract sentiment from article content
sentiment = blob.sentiment.polarity
# Add keywords and sentiment to article dictionary
article['keywords'] = keywords
article['sentiment'] = sentiment
article['date'] = article['dateAdded']
analyzed_articles.append(article)
return analyzed_articles
- Make a function to insert data into the BigQuery table.
>>> def insert_data(analyzed_articles):
# Define BigQuery table schema
table_ref = client.dataset('dataset-name').table('table-name')
schema = [
bigquery.SchemaField("article_id", "STRING", mode="REQUIRED"),
bigquery.SchemaField("title", "STRING", mode="REQUIRED"),
bigquery.SchemaField("date", "TIMESTAMP", mode="REQUIRED"),
bigquery.SchemaField("keywords", "STRING", mode="REPEATED"),
bigquery.SchemaField("sentiment", "FLOAT", mode="REQUIRED")
]
# Create BigQuery table partitioned on date
table = bigquery.Table(table_ref, schema=schema)
table.time_partitioning = bigquery.TimePartitioning(field="date")
table = client.create_table(table)
# Insert data into BigQuery table
rows_to_insert = []
for article in analyzed_articles:
rows_to_insert.append((article['_id'], article['title'],article['dateAdded'] ,article['keywords'], article['sentiment']))
errors = client.insert_rows(table, rows_to_insert)
if errors:
print(f"Errors inserting rows into BigQuery: {errors}")
else:
print(f"Rows inserted into BigQuery: {len(rows_to_insert)}")
- At last, define a function to execute the above function in order.
>>> def run():
articles = extract_articles()
analyzed_articles = analyze_articles(articles)
insert_data(analyzed_articles)
# Run main function
>>> if __name__ == "__main__":
run()
Conclusion
Through the above procedure, we can tell the sentiment of an article.
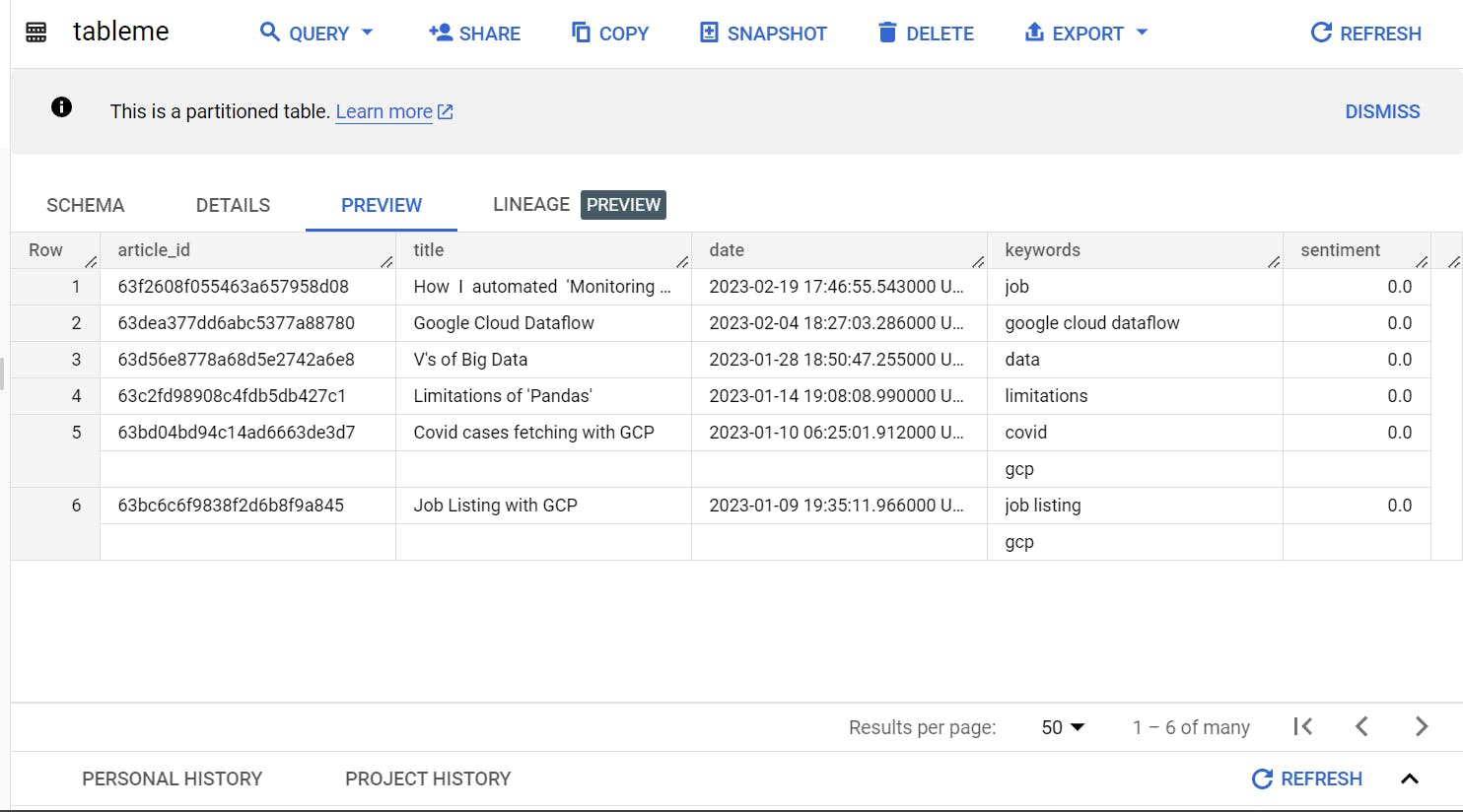
The above-explained things are just basic but we can explore more through them. Let me know if you have any ideas to explore this topic more.

